Entries Tagged as 'Drugs and Brain Disorders'
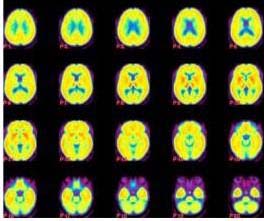 Methamphetamine is one of the most addictive and neurotoxic drugs of abuse and it produces large increases in dopamine, a brain chemical associated with feelings of pleasure and reward — both by increasing dopamine’s release from nerve cells and by blocking its reuptake.
Methamphetamine is one of the most addictive and neurotoxic drugs of abuse and it produces large increases in dopamine, a brain chemical associated with feelings of pleasure and reward — both by increasing dopamine’s release from nerve cells and by blocking its reuptake.
Using positron emission tomography (PET) to track tracer doses of methamphetamine in humans’ brains, scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Brookhaven National Laboratory found that meth was slow to clear the brain.
“This slow clearance of methamphetamine from such widespread brain regions may help explain why the drug has such long-lasting behavioral and neurotoxic effects.” Methamphetamine is known to produce lasting damage not only to dopamine cells but also to other brain regions, including white matter, that are not part of the dopamine network” stated chemist Joanna Fowler, lead author on the study.
[Read more →]
Tags: Drugs and Brain Disorders
 The proof every person must see about drugs, alcohol and the brain!
The proof every person must see about drugs, alcohol and the brain!
SEE FOR YOURSELF on DVD how drugs and alcohol damage your brain . . .
Meet five young people from different backgrounds, with different levels of substance abuse, including two who chose to stay clear of drugs or alcohol.
Hear their stories and learn about the impact their choices have had on the quality of their lives.
Next, look at the scans of their brains. See for yourself how their choices; good or bad; have affected the health of their brains.
The candid conversations between these young people and Dr. Daniel Amen, a pioneer in the use of brain scans, are revealing. They want to know if it’s too late . . . and they want another chance . . . now that they realize they DO have a choice.
The question echoes in their ears . . . Which Brain Do You Want?
This powerful, high-energy production includes . . .
* How the brain works
* How the brain is involved in everything you do
* What happens when the brain “misfires”
* The physical impact of drugs and alcohol on brain function
* How to improve your brain
I have this DVD and it is . . .
A MUST-SEE FOR PARENTS AND TEACHERS WHO WANT TEENS TO KNOW THE TRUTH ABOUT DRUGS AND ALCOHOL!
[Read more →]
Tags: Drugs and Brain Disorders
It compares normal brain images to abnormal brain images and looks at functional neuroanatomy.
[Read more →]
Tags: Drugs and Brain Disorders
Comparisons of normal brain images and brains that have been affected by alcohol and drugs.
[Read more →]
Tags: Drugs and Brain Disorders
 Studies have shown that people who take prescriptions for an anxiety disorder don’t get much help from it. And doctors have no definitive way to predict who will, and who won’t, benefit from each anti-anxiety prescription they write.
Studies have shown that people who take prescriptions for an anxiety disorder don’t get much help from it. And doctors have no definitive way to predict who will, and who won’t, benefit from each anti-anxiety prescription they write.
You are like a medical experiment or guinea pig.
K. Luan Phan, M.D., University of Michigan Medical School researcher, and his team are working to bring more certainty to how doctors and patients choose anxiety treatments, by probing the connection between brain activity, genetics and medication. According to the Journal of Neuroscience, he is reporting intriguing findings from brain imaging studies with marijuana users and making comparisons with prescription drugs such as Zoloft.
Dr. Phan notes that some individuals may be using illicit drugs and misusing prescribed drugs to alleviate their anxiety.
Wow – what a revelation! I call this self medication.
[Read more →]
Tags: Drugs and Brain Disorders
A series of studies at University of Florida over the past five years has shown that using the popular club drug Ecstasy, also called MDMA, and other forms of methamphetamine lead to the same type of brain changes, cell loss and protein fluctuations in the brain that occur after a person endures a sharp blow to the head, according to recent findings.
[Read more →]
Tags: Drugs and Brain Disorders
Electrical signals in the brain are sent using chemicals called neurotransmitters. All addictive drugs affect the production, release, or elimination of neurotransmitters. The major Neurotransmitters implicated in addiction are noted below.
Serotonin
Serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine or 5-HT) is synthesized from dietary tryptophan and its primary function is regulation of sleep and mood. Low levels of serotonin have been associated with mood disorders such as depression.
Medications called specific serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), such as Prozac and Zoloft, increase serotonin levels but can be very dangerous. You should consider taking the essential amino acid trytophan instead. Check with a holistic doctor for advice.
Norepinephrine (NE)
NE’s common function is associated with arousal and alertness. It is synthesized from the essential amino acid tyrosine. The levels of NE fluctuate throughout the day and therefore there are periods when we feel more awake and alert, while at other times we are tired and sleepy.
Certain drugs of abuse, such as stimulants or “uppers”, increase alertness and arousal and cause talkativeness, restlessness, and agitation because of their action on NE systems.
Dopamine
Dopamine release gives us the experience of pleasure and therefore causes us to want to repeat the behaviors necessary to acquire the reward in the future.
It’s interesting that amphetamine and cocaine both increase the amount of dopamine. However, cocaine achieves this action by preventing dopamine reuptake, while amphetamine helps to release more dopamine.
So, these drugs with similar effects produce their actions through entirely different processes. In turn, addiction to the two drugs may call for somewhat different types of addiction treatment.
GABA
Gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA) is synthesized from glutamate (an amino acid) and is found in very high concentrations throughout the brain. It is considered an “inhibitory neurotransmitter”. Because GABA has inhibitory effects on neurons, any drug that increases the actions of GABA will decrease general brain activity and can be considered a “downer” or depressant. Depressants include alcohol, sleeping pills such as Ambien, muscle relaxants such as Valium, and barbiturates such as Secobarbital. Some depressants are very powerful and can cause coma or death.
The Most Addictive Drugs
Different drugs have different effects on the neurotransmitters. For instance, cocaine and methamphetamine are much more addicting than THC (marijuana) because they increase dopamine levels more quickly and to a greater extent.
[Read more →]
Tags: Drugs and Brain Disorders · Street Drugs
Researchers have generally known that people with ADHD are more likely than others to smoke cigarettes and abuse alcohol, marijuana, cocaine and other drugs.
[Read more →]
Tags: Drugs and Brain Disorders · Street Drugs
Many people with ADD self-medicate (treat their underlying problems) with substances as a way to feel more focused, more together, less anxious, less depressed, less overwhelmed, and just generally better.
[Read more →]
Tags: Alcohol Addiction · Drugs and Brain Disorders · Marijuana Addiction
In studies of patients who had smoked marijuana, Dr. Daniel Amen found significant changes in brain activity, especially those who were heavy users. Decreased brain activity was found in the prefrontal cortex and temporal lobes.
[Read more →]
Tags: Drugs and Brain Disorders · Marijuana Addiction
 Methamphetamine is one of the most addictive and neurotoxic drugs of abuse and it produces large increases in dopamine, a brain chemical associated with feelings of pleasure and reward — both by increasing dopamine’s release from nerve cells and by blocking its reuptake.
Methamphetamine is one of the most addictive and neurotoxic drugs of abuse and it produces large increases in dopamine, a brain chemical associated with feelings of pleasure and reward — both by increasing dopamine’s release from nerve cells and by blocking its reuptake. The proof every person must see about drugs, alcohol and the brain!
The proof every person must see about drugs, alcohol and the brain! Studies have shown that people who take prescriptions for an anxiety disorder don’t get much help from it. And doctors have no definitive way to predict who will, and who won’t, benefit from each anti-anxiety prescription they write.
Studies have shown that people who take prescriptions for an anxiety disorder don’t get much help from it. And doctors have no definitive way to predict who will, and who won’t, benefit from each anti-anxiety prescription they write.