 Researchers led by Nora D. Volkow, MD, director of the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA), report evidence that Provigil (generic name, modafinil) might be more addictive than thought.
Researchers led by Nora D. Volkow, MD, director of the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA), report evidence that Provigil (generic name, modafinil) might be more addictive than thought.
The study was published in the March issue of the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA).
“There is an increasing use of this medication, and people have promoted the off-label use of stimulants and Provigil as cognitive enhancers with the belief that these drugs are safe”. “But these drugs have side effects, and their use without proper medical oversight could lead to abuse and addiction.”
[Read more →]
Tags: News - Addiction and Alternative Health
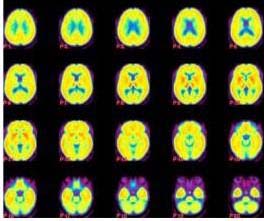 Methamphetamine is one of the most addictive and neurotoxic drugs of abuse and it produces large increases in dopamine, a brain chemical associated with feelings of pleasure and reward — both by increasing dopamine’s release from nerve cells and by blocking its reuptake.
Methamphetamine is one of the most addictive and neurotoxic drugs of abuse and it produces large increases in dopamine, a brain chemical associated with feelings of pleasure and reward — both by increasing dopamine’s release from nerve cells and by blocking its reuptake.
Using positron emission tomography (PET) to track tracer doses of methamphetamine in humans’ brains, scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Brookhaven National Laboratory found that meth was slow to clear the brain.
“This slow clearance of methamphetamine from such widespread brain regions may help explain why the drug has such long-lasting behavioral and neurotoxic effects.” Methamphetamine is known to produce lasting damage not only to dopamine cells but also to other brain regions, including white matter, that are not part of the dopamine network” stated chemist Joanna Fowler, lead author on the study.
[Read more →]
Tags: Drugs and Brain Disorders
 According to recent research, cigarette companies have manipulated the menthol content in cigarettes to lure young people into smoking.
According to recent research, cigarette companies have manipulated the menthol content in cigarettes to lure young people into smoking.
Menthol masks the harshness and irritation of cigarettes, allowing delivery of an effective dose of nicotine, the addictive chemical in cigarettes. There was a deliberate strategy to recruit and addict young smokers by adjusting menthol to create a milder experience for the first time smoker.
For example, Marlboro introduced Marlboro Milds in 2000, with a lower menthol concentration while raising the menthol content in Marlboro Menthol, favored by older smokers. Menthol brands with the greatest market share growth among young adults had the lowest menthol levels (Marlboro Milds and Newport) among the brands tested.
This is another example of the cynical behavior of the tobacco industry to hook teens and African Americans to a deadly addiction. This is after the industry told the American public it had changed its marketing practices.
[Read more →]
Tags: Smoking - Nicotine Addiction
Electrical signals in the brain are sent using chemicals called neurotransmitters. All addictive drugs affect the production, release, or elimination of neurotransmitters. The major Neurotransmitters implicated in addiction are noted below.
Serotonin
Serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine or 5-HT) is synthesized from dietary tryptophan and its primary function is regulation of sleep and mood. Low levels of serotonin have been associated with mood disorders such as depression.
Medications called specific serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), such as Prozac and Zoloft, increase serotonin levels but can be very dangerous. You should consider taking the essential amino acid trytophan instead. Check with a holistic doctor for advice.
Norepinephrine (NE)
NE’s common function is associated with arousal and alertness. It is synthesized from the essential amino acid tyrosine. The levels of NE fluctuate throughout the day and therefore there are periods when we feel more awake and alert, while at other times we are tired and sleepy.
Certain drugs of abuse, such as stimulants or “uppers”, increase alertness and arousal and cause talkativeness, restlessness, and agitation because of their action on NE systems.
Dopamine
Dopamine release gives us the experience of pleasure and therefore causes us to want to repeat the behaviors necessary to acquire the reward in the future.
It’s interesting that amphetamine and cocaine both increase the amount of dopamine. However, cocaine achieves this action by preventing dopamine reuptake, while amphetamine helps to release more dopamine.
So, these drugs with similar effects produce their actions through entirely different processes. In turn, addiction to the two drugs may call for somewhat different types of addiction treatment.
GABA
Gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA) is synthesized from glutamate (an amino acid) and is found in very high concentrations throughout the brain. It is considered an “inhibitory neurotransmitter”. Because GABA has inhibitory effects on neurons, any drug that increases the actions of GABA will decrease general brain activity and can be considered a “downer” or depressant. Depressants include alcohol, sleeping pills such as Ambien, muscle relaxants such as Valium, and barbiturates such as Secobarbital. Some depressants are very powerful and can cause coma or death.
The Most Addictive Drugs
Different drugs have different effects on the neurotransmitters. For instance, cocaine and methamphetamine are much more addicting than THC (marijuana) because they increase dopamine levels more quickly and to a greater extent.
[Read more →]
Tags: Drugs and Brain Disorders · Street Drugs
When tobacco is smoked, nicotine is absorbed by the lungs and quickly moves into the bloodstream and then reaches the brain within 8 seconds! Nicotine also acts directly on the heart to change heart rate and blood pressure and also on the nerves that control respiration to change breathing patterns.
[Read more →]
Tags: Smoking - Nicotine Addiction
According to a National Institute on Drug Abuse research report, there are three classes of prescription drugs that are most commonly abused:
1- opioids, which are most often prescribed to treat pain – examples include: codeine, oxycodone (OxyContin and Percocet), and morphine (Kadian and Avinza);
2- central nervous system (CNS) depressants, which are used to treat anxiety and sleep disorders – examples include: barbiturates (Mebaral and Nembutal) and benzodiazepines (Valium and Xanax);
3- stimulants, which are prescribed to treat the sleep disorder narcolepsy, attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), and obesity – examples include: dextroamphetamine (Dexedrine and Adderall) and methylphenidate (Ritalin and Concerta).
Many people benefit from the appropriate use of prescription pain killers, but, when abused, they can be as addictive and dangerous as illegal drugs. Prescription drugs should only be taken exactly as directed by a medical professional.
[Read more →]
Tags: Drug Addiction Alternative Treatment · Prescription Drugs Addiction
An addict usually has poor nutrition and that is why we consider a great nutrition plan a vital part of quitting smoking.
[Read more →]
Tags: Main · Smoking - Nicotine Addiction
 Researchers led by Nora D. Volkow, MD, director of the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA), report evidence that Provigil (generic name, modafinil) might be more addictive than thought.
Researchers led by Nora D. Volkow, MD, director of the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA), report evidence that Provigil (generic name, modafinil) might be more addictive than thought. Methamphetamine is one of the most addictive and neurotoxic drugs of abuse and it produces large increases in dopamine, a brain chemical associated with feelings of pleasure and reward — both by increasing dopamine’s release from nerve cells and by blocking its reuptake.
Methamphetamine is one of the most addictive and neurotoxic drugs of abuse and it produces large increases in dopamine, a brain chemical associated with feelings of pleasure and reward — both by increasing dopamine’s release from nerve cells and by blocking its reuptake. According to recent research, cigarette companies have manipulated the menthol content in cigarettes to lure young people into smoking.
According to recent research, cigarette companies have manipulated the menthol content in cigarettes to lure young people into smoking.