 Kathleen DesMaisons, PhD, was one of the speakers at the “Brain Repair” conference I attended last month. She is author of “Potatoes Not Prozac“, “The Sugar Addict’s Total Recovery Program” and others. She is the first person to receive a doctorate in addictive nutrition and has more than 30 years experience working in public health and nutrition.
Kathleen DesMaisons, PhD, was one of the speakers at the “Brain Repair” conference I attended last month. She is author of “Potatoes Not Prozac“, “The Sugar Addict’s Total Recovery Program” and others. She is the first person to receive a doctorate in addictive nutrition and has more than 30 years experience working in public health and nutrition.
Many people who suffer from sugar sensitivity don’t even know it and they continue to consume large quantities of sweets, breads, pasta, or alcohol. She says her research shows indulging in sugar highs should be treated much more seriously like heroin or alcohol dependency because sugar causes damage in various neurotransmitters just like those drugs and can eventually wreak your health and relationships.
Below are Dr. DesMaison’s seven steps that will free you from the Jekyll and Hyde Syndrome of sugar addiction.
7 Step Solution for Sugar Addiction
1. Eat breakfast with protein
2. Journal what you eat and how you feel
3. Eat three meals a day with protein (no more than 5 hours between meals)
4. Take the recommended vitamins and have a potato before bed
5. Shift from white foods to brown foods
6. Reduce or eliminate sugars
7. Create a new life
[Read more →]
Tags: Sugar Addiction
 The term addiction usually refers to the chronic use of one of three kinds of psychotropic substances, legal drugs (eg. alcohol, nicotine), illicit drugs (eg. cocaine, marijuana) or prescription drugs (eg. valium, prozac), in large enough quantities to cause life-damaging consequences in various aspects of one’s life.
The term addiction usually refers to the chronic use of one of three kinds of psychotropic substances, legal drugs (eg. alcohol, nicotine), illicit drugs (eg. cocaine, marijuana) or prescription drugs (eg. valium, prozac), in large enough quantities to cause life-damaging consequences in various aspects of one’s life.
Craving is the primary symptom of addiction, and if severe enough, an addict will destroy anyone or anything to get to the “substance” which they are deluded into believing will satisfy their craving and bring happiness.
Cause of Addiction
Biochemical imbalances in eight key neurotransmitters are the driving force behind all addictions. (Brain cells or neurons, produce chemical substances called neurotransmitters and they control virtually every aspect of your life by communication with other cells.) When they are deficient, the addicted person finds it extremely difficult to satisfy their cravings. Addicts become progressively powerless over the dictates of their imbalanced brain chemistry.
[Read more →]
Tags: Drug Addiction Alternative Treatment
 Amino-acid Therapy is a powerful natural means of healing and repair from drug abuse. This approach offers a highly effective alternative to standard addiction therapies.
Amino-acid Therapy is a powerful natural means of healing and repair from drug abuse. This approach offers a highly effective alternative to standard addiction therapies.
It is generally accepted that 20 amino acids are important to human nutrition for adults. They are the chemical units or “building blocks” of the body that make up proteins. They are all crucial to our health for repairing the body, promoting proper functioning of the blood, and enhancing communication within the brain and nervous system.
Amino acids are divided into two groups: essential and non-essential. Both types of amino acids are necessary for human functioning. The difference between the two groups is that essential amino acids are not synthesized by our bodies so it’s essential that we get them from another source. Because amino acids are not stored in the body like fats or carbohydrates, we have to consume them on a regular basis to maintain normal physical and mental health.
[Read more →]
Tags: Drug Addiction Alternative Treatment
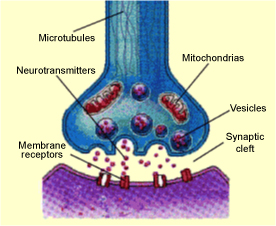 The term “drug addiction” is a disturbing word that brings to mind other words with equally unpleasant associations such as hopeless, out-of-control, desperate, inadequate, failure—you can no doubt add many more. Part of the reason the word is so upsetting is that for most people who try to overcome drug addiction, treatment options have been limited and often ineffective.
The term “drug addiction” is a disturbing word that brings to mind other words with equally unpleasant associations such as hopeless, out-of-control, desperate, inadequate, failure—you can no doubt add many more. Part of the reason the word is so upsetting is that for most people who try to overcome drug addiction, treatment options have been limited and often ineffective.
In fact, “conventional” drug addiction treatment programs have a success rate of 25% or less! One of the reasons I believe this to be the case is that these “conventional” programs do not adequately address the physiological basis of substance abuse; more specifically biochemical imbalances that occur in the brains of people with substance abuse issues. The good news is that solutions exist that do address these imbalances and offer hope to those seeking a more permanent solution.
According to Dr. C.E. Gant, author of “End Your Addiction Now”, “substance abuse problems are the result of biochemical imbalances that disrupt the normal workings of brain cells”. These imbalances are particularly important in the biochemistry of brain cells, or neurons. Neurons produce chemical substances called neurotransmitters (the brain’s messengers), and they control virtually every aspect of your life by communication with other cells.
Four key groups of “brain messengers” are related specifically to substance abuse. These particular messengers are vital to our ability to experience pleasure and satisfaction. The healthy functioning of these neurotransmitters is vital to our well-being and our ability to function in a productive manner. The four groups of neurotransmitters include endorphins and enkephalins, serotonin, GABA, and catacholamines.
[Read more →]
Tags: Drug Addiction Alternative Treatment
Community Addiction Recovery Association
(CARA)
This is a real life success story of how an organization is making a difference in society by offering an addiction treatment program that works.
 In 1995, under the leadership and vision of Carolyn Reuben, LAc, CARA became a 501(c)3 nonprofit organization and began providing acupuncture detoxification services at the Chemical Dependency Center for Women (now Strategies for Change).
In 1995, under the leadership and vision of Carolyn Reuben, LAc, CARA became a 501(c)3 nonprofit organization and began providing acupuncture detoxification services at the Chemical Dependency Center for Women (now Strategies for Change).
Since then CARA has added nutrition education, targeted nutritional supplements, healthy meal preparation, and several mind-body integration techniques.
CARA’s services are now provided at numerous facilities throughout the Sacramento Region, including Sacramento County’s Drug Court Program.
In an article printed in the January 2007 Townsend Letter, Carolyn Reuben stated:
“We believe that there is a disconnect between what science knows an addict needs and what society provides as treatment. Yes, addicts need behavior modification training. They also need mental health counseling. And a drug-free place to live, and a job with a living wage. Yet, even before all that, they need brain repair at the molecular level.”
Reuben continues and gives more details of the program.
[Read more →]
Tags: Drug Addiction Alternative Treatment
Electrical signals in the brain are sent using chemicals called neurotransmitters. All addictive drugs affect the production, release, or elimination of neurotransmitters. The major Neurotransmitters implicated in addiction are noted below.
Serotonin
Serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine or 5-HT) is synthesized from dietary tryptophan and its primary function is regulation of sleep and mood. Low levels of serotonin have been associated with mood disorders such as depression.
Medications called specific serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), such as Prozac and Zoloft, increase serotonin levels but can be very dangerous. You should consider taking the essential amino acid trytophan instead. Check with a holistic doctor for advice.
Norepinephrine (NE)
NE’s common function is associated with arousal and alertness. It is synthesized from the essential amino acid tyrosine. The levels of NE fluctuate throughout the day and therefore there are periods when we feel more awake and alert, while at other times we are tired and sleepy.
Certain drugs of abuse, such as stimulants or “uppers”, increase alertness and arousal and cause talkativeness, restlessness, and agitation because of their action on NE systems.
Dopamine
Dopamine release gives us the experience of pleasure and therefore causes us to want to repeat the behaviors necessary to acquire the reward in the future.
It’s interesting that amphetamine and cocaine both increase the amount of dopamine. However, cocaine achieves this action by preventing dopamine reuptake, while amphetamine helps to release more dopamine.
So, these drugs with similar effects produce their actions through entirely different processes. In turn, addiction to the two drugs may call for somewhat different types of addiction treatment.
GABA
Gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA) is synthesized from glutamate (an amino acid) and is found in very high concentrations throughout the brain. It is considered an “inhibitory neurotransmitter”. Because GABA has inhibitory effects on neurons, any drug that increases the actions of GABA will decrease general brain activity and can be considered a “downer” or depressant. Depressants include alcohol, sleeping pills such as Ambien, muscle relaxants such as Valium, and barbiturates such as Secobarbital. Some depressants are very powerful and can cause coma or death.
The Most Addictive Drugs
Different drugs have different effects on the neurotransmitters. For instance, cocaine and methamphetamine are much more addicting than THC (marijuana) because they increase dopamine levels more quickly and to a greater extent.
[Read more →]
Tags: Drugs and Brain Disorders · Street Drugs

Marijuana is the most frequently used illegal substance in many countries, including the United Kingdom and the United States and it seems to increase the chance of becoming psychotic, researchers report in an analysis of past research that brings up the old issue of whether pot is dangerous.
The new review suggests that even infrequent use of marijuana could raise the small but real risk of this serious mental illness by 40 percent.
Doctors have long suspected a connection and say the latest findings underline the need to highlight marijuana’s long-term risks. The research, paid for by the British Health Department, was published recently in the medical journal The Lancet. (thelancet.com)
“The available evidence now suggests that cannabis is not as harmless as many people think,” said Dr. Stanley Zammit, one of the study’s authors and a lecturer in the department of psychological medicine at Cardiff University.
[Read more →]
Tags: Marijuana Addiction
The main problem with smoking is that the main addicting chemical in cigarettes, nicotine, destroys three of the natural, “feel-good” brain chemicals called neurotransmitters. These three natural chemicals are of two types, excitatory and inhibitory. The excitatory neurotransmitters – catecholamines – pep us up. The inhibitory one – acetylcholine – relaxes us.
When your brain’s ability to make its natural nicotine-like substances (acetylcholine or catecholamines) is totally suppressed, you’re compelled to find the artificial chemical (nicotine) to fill those receptors in your brain. Something has to go in there to keep your mood even. The absence of anything to fill these receptors causes the unpleasant symptoms known as withdrawal. This is why nicotine is addictive.
So, the easiest way to quit smoking is to put the right supplements in the brain to get it chemically balanced and to get the neurotransmitters operating normally.
[Read more →]
Tags: Smoking - Nicotine Addiction
Speed, meth, chalk, crystal, ice, glass. These are all names for the drug methamphetamine. It comes in many different forms and is snorted, swallowed, injected, or smoked. The smokable form is known as “ice” or “crystal,” due to its appearance.
Meth is a powerful street drug. It acts by changing how the brain works. It also speeds up many functions in the body. It has a chemical structure that is similar to another drug called amphetamine. Methamphetamine can cause lots of harmful things, including inability to sleep, paranoia, aggressiveness, and hallucinations.
How Does Methamphetamine Cause its Effects?
[Read more →]
Tags: Drugs and Brain Disorders · Street Drugs
Just as we turn down the volume on a radio that is too loud, the brain adjusts to the overwhelming surges in dopamine (and other neurotransmitters) by producing less dopamine or by reducing the number of receptors that can receive and transmit signals. As a result, dopamine’s impact on the reward circuit of a drug abuser’s brain can become abnormally low, and the ability to experience any pleasure is reduced. This is why the abuser eventually feels flat, lifeless, and depressed, and is unable to enjoy things that previously brought them pleasure. Now, they need to take drugs just to bring their dopamine function back up to normal. And, they must take larger amounts of the drug than they first did to create the dopamine high – an effect known as tolerance.
How does long-term drug taking affect brain circuits?
[Read more →]
Tags: Drugs and Brain Disorders
 Kathleen DesMaisons, PhD, was one of the speakers at the “Brain Repair” conference I attended last month. She is author of “Potatoes Not Prozac“, “The Sugar Addict’s Total Recovery Program” and others. She is the first person to receive a doctorate in addictive nutrition and has more than 30 years experience working in public health and nutrition.
Kathleen DesMaisons, PhD, was one of the speakers at the “Brain Repair” conference I attended last month. She is author of “Potatoes Not Prozac“, “The Sugar Addict’s Total Recovery Program” and others. She is the first person to receive a doctorate in addictive nutrition and has more than 30 years experience working in public health and nutrition. The term addiction usually refers to the chronic use of one of three kinds of psychotropic substances, legal drugs (eg. alcohol, nicotine), illicit drugs (eg. cocaine, marijuana) or prescription drugs (eg. valium, prozac), in large enough quantities to cause life-damaging consequences in various aspects of one’s life.
The term addiction usually refers to the chronic use of one of three kinds of psychotropic substances, legal drugs (eg. alcohol, nicotine), illicit drugs (eg. cocaine, marijuana) or prescription drugs (eg. valium, prozac), in large enough quantities to cause life-damaging consequences in various aspects of one’s life.  Amino-acid Therapy is a powerful natural means of healing and repair from drug abuse. This approach offers a highly effective alternative to standard addiction therapies.
Amino-acid Therapy is a powerful natural means of healing and repair from drug abuse. This approach offers a highly effective alternative to standard addiction therapies. The term “drug addiction” is a disturbing word that brings to mind other words with equally unpleasant associations such as hopeless, out-of-control, desperate, inadequate, failure—you can no doubt add many more. Part of the reason the word is so upsetting is that for most people who try to overcome drug addiction, treatment options have been limited and often ineffective.
The term “drug addiction” is a disturbing word that brings to mind other words with equally unpleasant associations such as hopeless, out-of-control, desperate, inadequate, failure—you can no doubt add many more. Part of the reason the word is so upsetting is that for most people who try to overcome drug addiction, treatment options have been limited and often ineffective. 
