September 22nd, 2009 · No Comments
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has shown new signs of regulating the tobacco industry by placing a federal ban on flavored cigarettes effective September 22, 2009.
This means that it is illegal to manufacture, import, market or distribute candy, fruit and all flavored cigarettes. According to health and federal authorities, flavored cigarettes are more appealing to youth and simply encourages smoking. It doesn’t take a ‘rocket scientist’ to see that flavored cigarettes are a gateway for children and young adults to become addicted to tobacco/nicotine.
[Read more →]
Tags: News - Addiction and Alternative Health
 The US Senate voted today (June 11, 2009) to give the FDA new power to limit nicotine in cigarettes, drastically curtail ads and ban candied tobacco products aimed at young people.
The US Senate voted today (June 11, 2009) to give the FDA new power to limit nicotine in cigarettes, drastically curtail ads and ban candied tobacco products aimed at young people.
The legislation, one of the most dramatic anti-smoking initiatives since the U.S. surgeon general’s warning 45 years ago that tobacco causes lung cancer, would give the Food and Drug Administration authority to regulate the content, marketing and advertising of cigarettes and other tobacco products.
“This legislation represents the strongest action Congress has ever taken to reduce tobacco use, the leading preventable cause of death in the United States,” declared Matthew Myers, president of Campaign for Tobacco-free Kids.
[Read more →]
Tags: News - Addiction and Alternative Health
The theme of World No Tobacco Day 2009 is "Tobacco Health Warnings", with an emphasis on the picture warnings that have been shown to be particularly effective at making people aware of the health risks of tobacco use and convincing them to quit.
[Read more →]
Tags: News - Addiction and Alternative Health
A federal appeals court on May 22,2009, agreed with the major elements of a 2006 landmark ruling that found the nation's top tobacco companies guilty of racketeering and fraud for deceiving the public about the dangers of smoking.
[Read more →]
Tags: News - Addiction and Alternative Health
 Nicotine isn’t just addictive. It probably interferes with dozens of bodily functions according to an article published April 3 in the Journal of Proteome Research.
Nicotine isn’t just addictive. It probably interferes with dozens of bodily functions according to an article published April 3 in the Journal of Proteome Research.
“It opens several new lines of investigation,” said lead author Edward Hawrot, professor of molecular science, molecular pharmacology, physiology and biotechnology at Brown University.
Hawrot’s research set out to provide a more basic understanding of how nicotine affects the process of cell communication through the nervous system.
The Brown University researchers looked specifically at the alpha-7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor.
Their discovery: 55 proteins were found to interact with the alpha-7 nicotinic receptor. Scientists had not previously known of those connections.
[Read more →]
Tags: Smoking - Nicotine Addiction
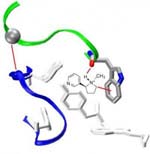 This molecular model shows nicotine (in center) binding to a brain receptor via a cation-À interaction. (Image Credit: Caltech/Dennis Dougherty) According to California Institute of Technology (Caltech) researchers, lead by Dennis Dougherty, Professor of Chemistry, there is a very small genetic difference between brain cells and muscle cells that alter the way that nicotine affects us.
This molecular model shows nicotine (in center) binding to a brain receptor via a cation-À interaction. (Image Credit: Caltech/Dennis Dougherty) According to California Institute of Technology (Caltech) researchers, lead by Dennis Dougherty, Professor of Chemistry, there is a very small genetic difference between brain cells and muscle cells that alter the way that nicotine affects us.
The receptor nicotine binds to in the brain’s neurons–a type of acetylcholine receptor, which also binds the neurotransmitter acetylcholine–is found in large numbers in muscle cells. Were nicotine to bind with those cells, it would cause muscles to contract with such force that the response would likely prove lethal.
The cause of this difference in binding potency, says Dougherty, is a single point mutation that occurs in the receptor near the key tryptophan amino acid that makes the cation-A interaction. “This one mutation means that, in the brain, nicotine can cozy up to this one particular tryptophan much more closely than it can in muscle cells,” he explains. “And that is what allows the nicotine to make the strong cation-À interaction.”
[Read more →]
Tags: Smoking - Nicotine Addiction
 Smoking can have numerous negative effects. Information gathered from various research studies point that out.
Smoking can have numerous negative effects. Information gathered from various research studies point that out.
In one such study, Dr. Gary Shaw of the March of Dimes and colleagues from institutes in Norway, Holland, and Texas, studied serum samples collected between 2003 and 2005 from pregnant women enrolled in the California Expanded AFP (alpha fetoprotein) program. The researchers measured the levels of cotinine, a metabolite of nicotine, to determine whether the mothers smoked during pregnancy. They found that women who smoked during pregnancy were nearly 2.5 times more likely to have babies with oral clefts.
According to Dr. Shaw, “Babies with oral clefts require significant medical care. Often necessary are four surgeries by age two, and they may have speech, hearing, and feeding problems.”
In a related study, Dr. Laura Stroud and colleagues from Brown University studied the effects of cigarette smoke exposure on infant behavior. The researchers studied 56 otherwise healthy infants and used questionnaires and cotinine measurements to determine cigarette smoke exposure. They found that the 28 babies who had been exposed to cigarette smoke were more irritable and difficult to sooth.
[Read more →]
Tags: Smoking - Nicotine Addiction
 From past research, it’s known that the children of mothers who smoked during pregnancy are at greater risk of ADHD (Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder).
From past research, it’s known that the children of mothers who smoked during pregnancy are at greater risk of ADHD (Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder).
Young people with ADHD are not only at increased risk of starting to smoke cigarettes, they also tend to become more seriously addicted to nicotine and more vulnerable to environmental factors such as having friends or parents who smoke.
It appears that those with more ADHD related symptoms such as prominent inattention, distraction, overactivity or impulsivity of the smokers, the more serious their dependence on nicotine.
Dr. Timothy Wilens, Associate Professor of Psychiatry at Harvard Medical School and co-author of a recent study, stated that, “it looks like interplay between the dopamine system, more substantially related to ADHD and addiction, and the cholinergic system related to smoking is probably important”. (The study was supported in part by the National Institute on Drug Abuse.)
[Read more →]
Tags: Smoking - Nicotine Addiction
September 28th, 2008 · No Comments
 Once you start smoking it is hard to stop because the nicotine contained in tobacco products is so quickly addictive and is even considered to be as addictive as heroin or cocaine.
Once you start smoking it is hard to stop because the nicotine contained in tobacco products is so quickly addictive and is even considered to be as addictive as heroin or cocaine.
Why?
When a cigarette is smoked, nicotine-rich blood passes from the lungs to the brain within 7 – 10 seconds and immediately stimulates the release of many neurotransmitters including dopamine (pleasurable feeling).
It is important to note that nicotine is very powerful and poisonous for the nervous system. There is enough (50 mg) in four cigarettes to kill a person within just minutes if it were injected directly into the bloodstream.
The problem is the effects from smoking are short-lived, lasting only a few minutes to a couple of hours. This leads people to smoke throughout the day to dose themselves with this deadly chemical because they want to continue to have whatever positive effects they think they are receiving. Add to this the fact that you can become tolerant to nicotine’s effects — you need to use more and more of it to reach the same degree of stimulation or relaxation — and you can see how people would quickly move from smoking one cigarette to a pack a day habit.
A typical smoker will take 10 draws on a cigarette over a period of 5 minutes. Therefore, a person who smokes about 1-½ packs (30 cigarettes) daily, is getting 300 “hits” of nicotine to the brain each day.
[Read more →]
Tags: Smoking - Nicotine Addiction
 Herbal medicines can be part of a vital and successful strategy to combat addictions. They can be used to calm nerves, fight depression, detoxify, and help restore damaged organs and encourage healthy life choices.
Herbal medicines can be part of a vital and successful strategy to combat addictions. They can be used to calm nerves, fight depression, detoxify, and help restore damaged organs and encourage healthy life choices.
Here are some examples:
* Milk Thistle – Especially helpful in the support of the liver, helping to cleanse toxins and encourages new cell growth.
* Lobelia – helps reduce craving for nicotine
* Oatstraw – Helps to rebalance the levels of endorphins.
* St. Johns Wort – For use as an anti-depressant.
* Valerian – Acts as a good sedative and helps relax the central nervous system and decrease levels of anxiety and stress
[Read more →]
Tags: Drug Addiction Alternative Treatment
 The US Senate voted today (June 11, 2009) to give the FDA new power to limit nicotine in cigarettes, drastically curtail ads and ban candied tobacco products aimed at young people.
The US Senate voted today (June 11, 2009) to give the FDA new power to limit nicotine in cigarettes, drastically curtail ads and ban candied tobacco products aimed at young people. Nicotine isn’t just addictive. It probably interferes with dozens of bodily functions according to an article published April 3 in the Journal of Proteome Research.
Nicotine isn’t just addictive. It probably interferes with dozens of bodily functions according to an article published April 3 in the Journal of Proteome Research. This molecular model shows nicotine (in center) binding to a brain receptor via a cation-À interaction. (Image Credit: Caltech/Dennis Dougherty) According to California Institute of Technology (Caltech) researchers, lead by Dennis Dougherty, Professor of Chemistry, there is a very small genetic difference between brain cells and muscle cells that alter the way that nicotine affects us.
This molecular model shows nicotine (in center) binding to a brain receptor via a cation-À interaction. (Image Credit: Caltech/Dennis Dougherty) According to California Institute of Technology (Caltech) researchers, lead by Dennis Dougherty, Professor of Chemistry, there is a very small genetic difference between brain cells and muscle cells that alter the way that nicotine affects us. Smoking can have numerous negative effects. Information gathered from various research studies point that out.
Smoking can have numerous negative effects. Information gathered from various research studies point that out. From past research, it’s known that the children of mothers who smoked during pregnancy are at greater risk of ADHD (Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder).
From past research, it’s known that the children of mothers who smoked during pregnancy are at greater risk of ADHD (Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder). Once you start smoking it is hard to stop because the nicotine contained in tobacco products is so quickly addictive and is even considered to be as addictive as heroin or cocaine.
Once you start smoking it is hard to stop because the nicotine contained in tobacco products is so quickly addictive and is even considered to be as addictive as heroin or cocaine. Herbal medicines can be part of a vital and successful strategy to combat addictions. They can be used to calm nerves, fight depression, detoxify, and help restore damaged organs and encourage healthy life choices.
Herbal medicines can be part of a vital and successful strategy to combat addictions. They can be used to calm nerves, fight depression, detoxify, and help restore damaged organs and encourage healthy life choices.